

MICROWATER THEORY
Why we get sick
Oxygen: Too much of a good thing?
Oxygen is essential to survival. It is relatively stable in the air, but when too much is absorbed into the body it can become active and unstable and has a tendency to attach itself to any biological molecule, including molecules of healthy cells. The chemical activity of these free radicals is due to one or more pairs of unpaired electrons.
About 2% of the oxygen we normally breathe becomes active oxygen, and this amount increases to approximately 20% with aerobic exercise.
 Such free radicals with unpaired electrons are unstable and have a high oxidation
potential, which means they are capable of stealing electrons from other cells. This
chemical mechanism is very useful in disinfectants such as hydrogen peroxide and
ozone which can be used to sterilize wounds or medical instruments. Inside the body
these free radicals are of great benefit due to their abiility to attack and eliminate
bacteria, viruses and other waste products.
Such free radicals with unpaired electrons are unstable and have a high oxidation
potential, which means they are capable of stealing electrons from other cells. This
chemical mechanism is very useful in disinfectants such as hydrogen peroxide and
ozone which can be used to sterilize wounds or medical instruments. Inside the body
these free radicals are of great benefit due to their abiility to attack and eliminate
bacteria, viruses and other waste products.
Active Oxygen in the body
Problems arise, however, when too many of these free radicals are turned loose in the body where they can also damage normal tissue.
Putrefaction sets in when microbes in the air invade the proteins, peptides, and amino acids of eggs, fish and meat. The result is an array of unpleasant substances such as:
- Hydrogen sulfide
- Ammonia
- Histamines
- Indoles
- Phenols
- Scatoles
These substances are also produced naturally in the digestive tract when we digest food, resulting in the unpleasant odor evidenced in feces. Putrefaction of spoiled food is caused by microbes in the air; this natural process is duplicated in the digestive tract by intestinal microbes. All these waste products of digestion are pathogenic, that is, they can cause disease in the body.
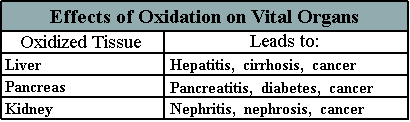
Hydrogen sulfide and ammonia are tissue toxins that can damage the liver. Histamines contribute to allergic disorders such as atopic dermatitis, urticaria (hives) and asthma. Indoles and phenols are considered carcinogenic.
Because waste products such as hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, histamines, phenols and indoles are toxic, the body's defense mechanisms try to eliminate them by releasing neutrophils (a type of leukocyte, or white corpuscle). These neutrophils produce active oxygen, oddball oxygen molecules that are capable of scavenging disintegrating tissues by gathering electrons from the molecules of toxic cells.
Problems arise, however, when too many of these active oxygen molecules, or free radicals, are produced in the body. They are extremely reactive and can also attach themselves to normal, healthy cells and damage them genetically. These active oxygen radicals steal electrons from normal, healthy biological molecules. This electron theft by active oxygen oxidizes tissue and can cause disease.
Because active oxygen can damage normal tissue, it is essential to scavenge this active oxygen from the body before it can cause disintegration of healthy tissue. If we can find an effective method to block the oxidation of healthy tissue by active oxygen, then we can attempt to prevent disease.




Antioxidants block dangerous oxidation
One way to protect healthy tissue from the ravages of oxidation caused by active oxygen is to provide free electrons to active oxygen radicals, thus neutralizing their high oxidation potential and preventing them from reacting with healthy tissue.
Research on the link between diet and cancer is far from complete, but some evidence indicates that what we eat may affect our susceptibility to cancer. Some foods seem to help defend against cancer, others appear to promote it.
Much of the damage caused by carcinogenic substances in food may come about because of an oxidation reaction in the cell. In this process, an oddball oxygen molecule may damage the cell's genetic code. Some researchers believe that substances that prevent oxidation -- called ANTIOXIDANTS -- can block the damage. This leads naturally to the theory that the intake of natural antioxidants could be an important aspect of the body's defense against cancer. Substances that some believe inhibit cancer include vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, selenium, and gluthione (an amino acid). These substance are reducing agents. They supply eletrons to free radicals and block the interaction of the free radical with normal tissue.
How we can avoid illness
As we mentioned earlier, the presence of toxic waste products such as hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, histamines, indoles, phenols and scatoles impart an offensive odor to human feces. In the medical profession, it is well known that patients suffering from hepatitis and cirrhosis pass particularly odoriferous stools.
Excessively offensive stools caused by the presence of toxins are indicators of certain diseases, and the body responds to the presence of these toxins by producing neutrophil leukocytes to release active oxygen in an attempt to neutralize the damage to organs that can be caused by such waste products. But when an excess amount of such active oxygen is produced, it can damage healthy cells as well as neutralize toxins. This leads us to the conclusion that we can minimize the harmful effect of these active oxygen radicals by reducing them with an ample supply of electrons.
Water . . . the natural solution
There is no substitute for a healthy balanced diet, especially rich in antioxidant materials such as vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, and other foods that are good for us. However, these substances are not the best source of free electrons that can block the oxidation of healthy tissue by active oxygen.
Water treated by electrolysis to increase its reduction potential is the best solution to the problem of providing a safe source of free electrons to block the oxidation of normal tissue by free oxygen radicals. We believe that reduced water, water with an excess of free electrons to donate to active oxygen, is the best solution because:
- The reduction potential of water can be dramatically increased over other antioxidants
in food or vitamin supplements.
- The molecule weight of reduced water is low, making it fast acting and able to reach all tissues of the body in a very short time.
What is Microwater
Microwater is the product of mild electrolysis which takes place in the Microwater unit. The production of Microwater, its properties, and how it works in the human body are described in the next section. Microwater is treated tap water that has not only been filtered, but has also been reformed in that it provides reduced water with a large mass of electrons that can be donated to active oxygen in the body to block the oxidation of normal cells.

Proceed to page 3.
Microwater Menu page
NOTE:
Dr. Hayashi is a Heart Specialist and Director of the Water Institute of Japan.
Dr. Hayashi has no affiliation with "Total Health Marketing",
or "Microwater Systems".