

USING MICROWATER
What Microwater Does
The microwater unit produces two kinds of water with different redox potentials, one with a high reduction potential and the other with a high oxidation potential.
Reduced Water
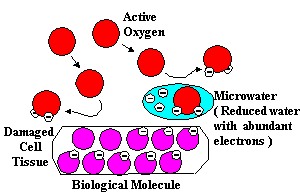
When taken internally, the reduced microwater with its redox potential of -250 to -350 mV readily donates its electrons to oddball oxygen radicals and blocks the interaction of the active oxygen with normal molecules.
A biological molecule (BM) remains intact and undamaged.
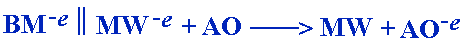
Undamaged biological molecules are less susceptible to infection and disease. The microwater gives up an extra electron and reduces the active oxygen (AO), thus rendering it harmless. The AO is reduced without damaging surrounding biological molecules. Substances which have the ability to counteract active oxygen by supplying electrons are called scavengers. Reduced water, therefore, can be called scavenging water.
When taken internally, the effects of reduced water are immediate. Microwater inhibits excessive fermentation in the digestive tract by reducing indirectly metabolites such as hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, histamines, indoles, phenols and scatoles, resulting in a cleaner stool within days after reduced water is taken on a regular basis. In 1965 the Ministry of Welfare of Japan announced that reduced water obtained from electrolysis can prevent abnormal fermentation of intestinal microbes.
Oxidized Water
Oxidized water with its redox potential of +700 to +800 mV is an oxidizing agent that can withdraw electrons from bacteria and kill them. The oxidized water from the Microwater unit can be used to clean hands, kitchen utensils, fresh vegetables and fruits, and to sterilize cutting boards and minor wounds. Tests have shown that oxidized water can be used effectively to treat athlete's foot, minor burns, insect bites, scratches, and so on.Dr. Yoshiaki Matsuo, Vice Director of the Water Institute of Japan, has developed another apparatus capable of producing hyperoxidized water with a redox potential of +1,050 mV or more, and a pH lower than 2.7. Tests have shown that this hyper oxidized water can quickly destroy MRSA (Methecillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus).
Although hyperoxidized water is a powerful sterilizing agent, it won't harm the skin. In fact, it can be used to heal. Hyperoxidized water has proven effective in Japanese hospitals in the treatment of bedsores and operative wounds with complicated infections.
But perhaps the most exciting future application of hyperoxidized water is in the field of agriculture where it has been used effectively on plants to kill fungi and other plant diseases. Hyperoxidized water is non-toxic, so agricultural workers can apply it without wearing special protective equipment because there is no danger of skin or respiratory damage. An added benefit of using hyperoxidized water to spray plants is that there is no danger to the environment caused by the accumulation of toxic chemicals in the ground.
Microwater superior to antioxidant diet
Today we read much about correct dieting principles and paying attention to what we eat in order to stay healthy. This is a sensible practice, but it is surprising that many of us don't realize that the bulk of what eat is composed of water. Vegetables and fruits are 90% water; fish and meat are about 70% water as well.Even advocates of the importance of vitamin C in diet staples have to admit that its potency, namely, the redox potential of this important vitamin, rapidly diminishes with age and preparation for the dining table. Carbohydrates, the main consistent of vegetables and fruit, has a molecular weight of 180 whereas water has a much lower molecular weight of 18.
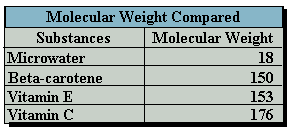
Microwater, with its low molecular weight and high reduction potential, makes it a superior scavenging agent of active oxygen. But electrolysis inside the Microwater unit not only charges the reduced water with electrons, it also reduces the size of reduced water molecule clusters.
NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) analysis reveals that tap water and well water consists of clusters of 10 to 13 H20 molecules. Electrolysis of water in the Microwater unit reduces these clusters to about half their normal size -- 5 to 6 water molecules per cluster.
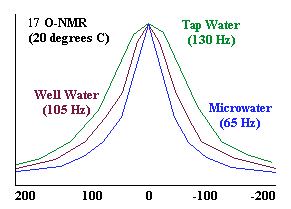
As the graph shows, the NMR signal that measures cluster size by line width at half-amplitude shows 65 Hz for reduced water and 133 Hz for tap water, revealing that the reduced water clusters are approximately half the size of tap water clusters.
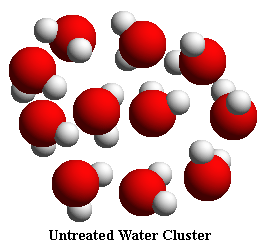
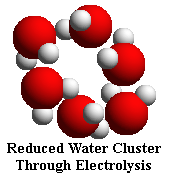
This is why Microwater is more readily absorbed by the body than untreated tap water. Microwater quickly permeates the body and blocks the oxidation of biological molecules by donating its abundant electrons to active oxygen, enabling biological molecules to replace themselves naturally without damage caused by oxidation that can cause diseases.

Proceed to page 5.
Microwater Menu page
NOTE:
Dr. Hayashi is a Heart Specialist and Director of the Water Institute of Japan.
Dr. Hayashi has no affiliation with "Total Health Marketing",
or "Microwater Systems".